3171. Point within a circle
Check, if the point is
inside the circle.
Input. The first line contains the
coordinates of the circle center and its radius. The second line contains the
coordinates of point A. All numbers are integers not exceeding 10000 by absolute
value.
Output. Print YES, if the
point A belongs to a circle (with boundaries), and NO otherwise.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
2 1 2 1 3 |
NO |
SOLUTION
geometry
Algorithm analysis
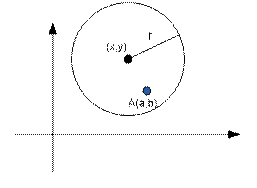
Let (x, y) be the coordinates of the
center of the circle and r be its
radius. Let (a, b) be the coordinates of point A. Point A lies inside
the circle (including boundaries) if
(x a)2
+ (y b)2 ≤ r2
Algorithm realization
Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d %d",&x,&y,&r);
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
Check if point (a, b) lies inside the circle.
if ((x - a)*(x - a) + (y - b)*(y - b) <= r*r)
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
Algorithm realization structures
#include <stdio.h>
int x, y, r, a, b;
struct circle
{
int x, y,
r;
} c;
struct point
{
int x, y;
} p;
int inside(struct point p, struct circle c)
{
return ((c.x - p.x)*(c.x - p.x) + (c.y - p.y)*(c.y - p.y) <= c.r * c.r);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d %d",
&c.x, &c.y, &c.r);
scanf("%d %d",
&p.x, &p.y);
if
(inside(p, c))
puts("YES");
else
puts("NO");
return 0;
}
Algorithm realization classes
#include <stdio.h>
class Point
{
public:
double x, y;
Point(double
x, double y) : x(x), y(y) {}
};
class Circle
{
public:
double x, y,
r;
Circle(double
x, double y, double
r) : x(x), y(y), r(r) {}
int
Inside(Point &p)
{
return (x -
p.x)*(x - p.x) + (y - p.y)*(y - p.y) <= r * r;
}
};
double x, y, r, a, b;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%lf
%lf %lf",&x,&y,&r);
Circle c(x,y,r);
scanf("%lf
%lf",&a,&b);
Point p(a,b);
if
(c.Inside(p)) puts("YES"); else puts("NO");
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = con.nextInt();
int y = con.nextInt();
int r = con.nextInt();
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
if ((x - a)*(x - a) + (y - b)*(y - b) <= r*r)
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
con.close();
}
}
Java realization classes
import java.util.*;
class Point
{
int x, y;
Point(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class Circle
{
int x, y, r;
Circle(int x, int y, int r)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.r = r;
}
boolean Inside(Point p)
{
return (x - p.x)*(x - p.x) + (y - p.y)*(y - p.y) <= r * r;
}
};
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = con.nextInt();
int y = con.nextInt();
int r = con.nextInt();
Circle c = new Circle(x,y,r);
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
Point p = new Point(a,b);
if (c.Inside(p))
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
con.close();
}
}